About NeGP
Over the years, an oversized range of initiatives has been undertaken by varied State Governments associated Central Ministries to begin an era of e-Government. Sustained efforts have been made at multiple levels to improve the delivery of public services and simplify the process of accessing them.
e-Governance in India
e-Governance in India has steadily evolved from computerization of state Departments to initiatives that encapsulate the finer points of Governance, like subject centricity, service orientation, and transparency. Lessons from previous e-Governance initiatives have played an important role in shaping the progressive e-Governance strategy of the country. For this reason, it has been considered that in order to accelerate the implementation of e-governance in various government arms at national, state and local level, a program approach should be adopted, which should be directed by general vision and strategy. In this approach, the core and support are the ability to save large costs through the distribution of infrastructure, thereby enabling the difference through standards, and to present the government with a conspicuous vision for citizens.
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP)
The National e-Governance Plan (NeGP), takes a holistic view of e-Governance initiatives across the country, integrating them into a collective vision, a shared cause. Around this idea, large-scale infrastructure is reaching villages far and wide, and in order to enable easy, reliable access to the Internet, large-scale digitization of records is underway. The ultimate objective is to bring public services closer home to citizens, as articulated in the Vision Statement of NeGP.
“All Government services reachable to the common man in his local area, through common service supplier, ofand guarantee efficiency, transparency, and reliableness of such services at cheap prices to appreciate the essential needs of the common man”
The Government approved the National e-Governance Plan (NeGP), comprising of 31 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and 8 components, on May 18, 2006. vision, approach, strategy, key components, implementation methodology, and management structure for NeGP has approved by The Government. However, the approval of NeGP does not constitute financial approval(s) for all the Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) and components under it. The extent or running projects of MMP category is implemented by different Central Ministries, States, and States Department will be suitably augmented and enhanced to align with the aim of NeGP.
e-Kranti is an essential pillar of the Digital India initiative. Considering the essential need fore-Governance, mobile Governance, and Smart Governance within the country, the approach and key elements of e-Kranti are approved by the Union cabinet on 25.03.2015 with the vision of “Transforming e-Governance for Transforming Governance”.
All new and on-going eGovernance projects as well as the existing projects, which are being revamped, should now follow the objective principles of e-Kranti namely ‘Transformation and not Translation’, ‘Integrated Services and not Individual Services’, ‘Government process Reengineering (GPR) to be obligatory in each MMP’, ‘ICT Infrastructure on Demand’, ‘Cloud by Default’, ‘Mobile First’, ‘Fast following Approvals’, ‘Mandating Standards and Protocols’, ‘Language Localization’, ‘National GIS (Geo-Spatial information System)’, ‘Security and Electronic data Preservation’.
There are 44 Mission Mode Projects under e-Kranti, which are at various stages of implementation.
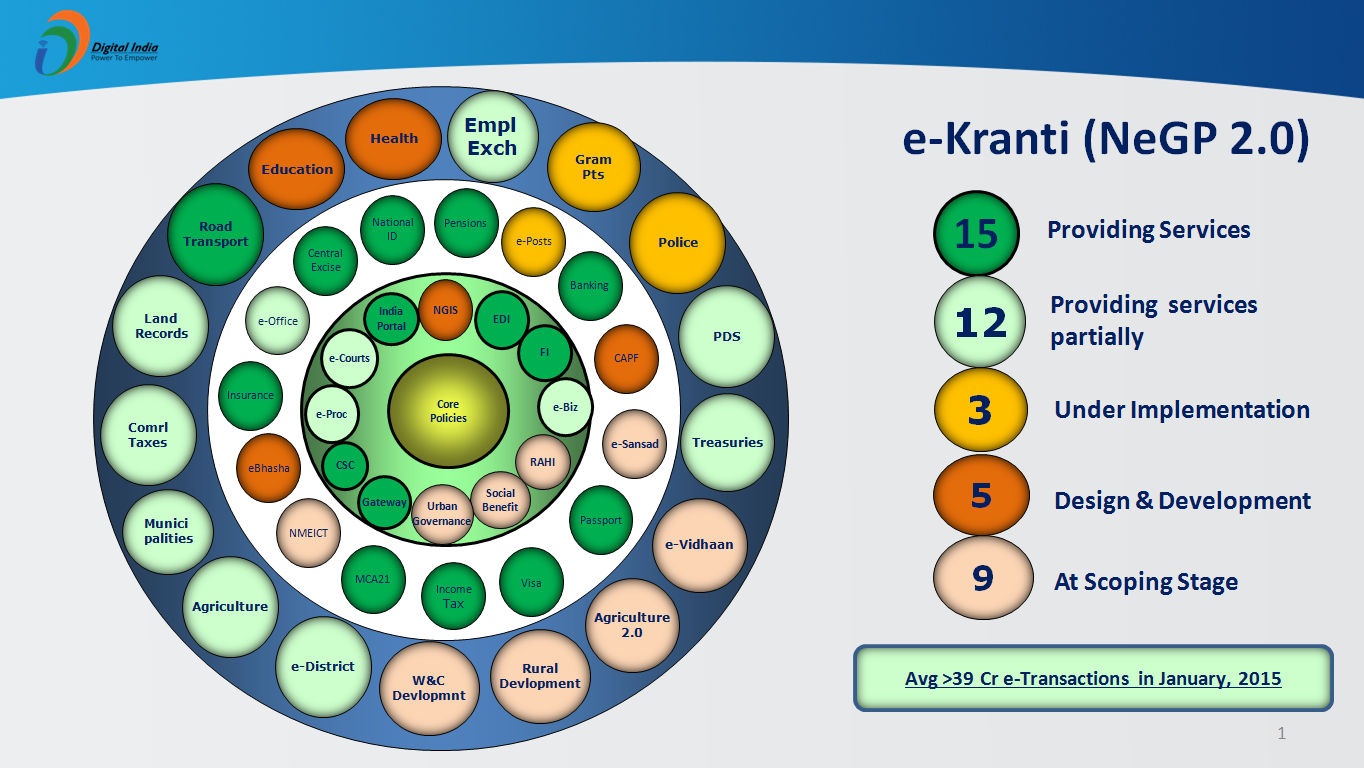
e-Transaction counts have been taken from the e-Taal (Electronic Transaction Aggregation & Analysis Layer) portal. E-Taal is a portal for dissemination of statistics related to electronic transactions under national and state level e-governance projects including MMPs. It receives dealing statistics from net primarily based applications sporadically on the close to real time basis. eTaal presents a fast analysis of dealing counts in tabular and graphical kind.
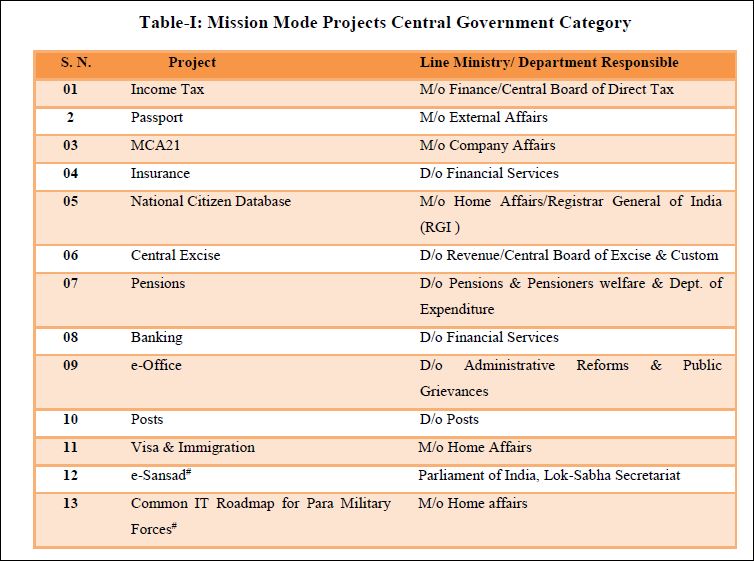
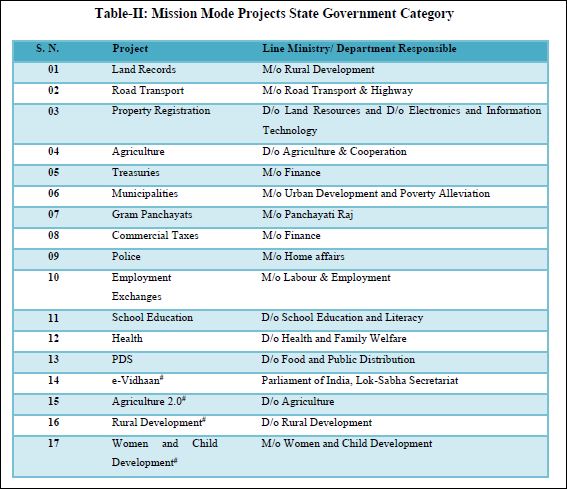
| Sl. No. | Project | Line Ministry/ Department Responsible |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | EDI (E-Commerce) | M/o Commerce & Industry |
| 02 | E-Biz | D/o Industrial Policy & Promotion |
| 03 | Common Services Centres | D/o Electronics and Information Technology |
| 04 | India Portal | D/o Electronics and Information Technology and D/o Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances |
| 05 | E-Courts | D/o Justice |
| 06 | E-Procurement | M/o Commerce & Industry/ DGS&D |
| 07 | National Service Delivery Gateway | D/o Electronics and Information Technology |
| 08 | Financial Inclusion# | D/o Financial Services |
| 09 | National Geographical Information System# | D/o Science & Technology |
| 10 | Social Benefits# | M/o Social Justice and Empowerment as the leader and other welfare departments as co-owners |
| 11 | Roads and Highways Information System (RAHI) # | M/o Road Transport & Highways |
| 12 | e-Bhasha # | D/o Electronics and Information Technology |
| 13 | National Mission on Education Through ICT (NMEICT) # | D/o Higher Education |
| 14 | Urban Governance # | Ministry of Urban Development |
Technology for Education – e-Education
All Schools will be connected with broadband. Free wifi will be provided in all secondary and higher secondary schools (coverage would be around 250,000 schools). A program on digital accomplishment would be preoccupied at the national level. massive On-line Open Courses (MOOCs) shall be developed and leveraged for e-Education.
Technology for Health – e-Healthcare
e-Healthcare would cover online medical consultation, online medical records, online medicine supply, pan-India exchange for patient information, etc. Pilots shall be undertaken in 2015 and full coverage would be provided in 3 years.
Technology for Farmers
This would facilitate farmers to get real- time price information, online ordering of inputs and online cash, loan, and relief payment with mobile banking.
Technology for Security
Mobile-based emergency services and disaster-related services will be provided on a real-time basis so that precautions should be taken in a timely manner and reducing the loss of lives and property.
Technology for Justice
Interoperable Criminal Justice System shall be strengthened by leveraging several related applications, i.e. e-Courts, e-Police, e-Jails, and e-Prosecution.
Technology for Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion shall be strengthened using mobile banking, Micro-ATM program, and CSCs/ Post Offices.
Technology for Cyber Security
National Cyber Security Co-ordination Centre would be set up to ensure safe and secure cyberspace within the country.
Credit- Digital India